Every surgical procedure generates certain nervousness and stress in the patient, which is why the performance of adequate sedation is essential and necessary for the patient and for the correct development of the surgery. Within the specialty of Maxillofacial Surgery there are different types of medium complexity interventions that can be performed on an outpatient basis without the need for hospitalization (genioplasties, SARPE, rhinoplasties, zygomatic implant surgery, wisdom tooth surgery, bone regeneration surgeries, etc.).
The ambulatory surgical circuit has great benefits for the patient:
- greater agility in performing the treatment
- lower overall economic cost
- less complexity of the surgery itself
However, to be able to carry out an outpatient surgery, a series of conditions must be met that guarantee the greatest safety and comfort for the patient, such as the use of minimally invasive surgical approaches, the use of intravenous sedation techniques and adequate infiltration with local anesthetics.
Is the same type of anesthetic used for everyone?

No. To know exactly the type and amount of anesthetics needed in each case, a preoperative assessment of the patient is made, which is performed in the same way as for surgical procedures performed in the operating room. This assessment consists of several steps:
- A physical examination of the patient and a thorough study of their medical history.
- Assessment of allergies, toxic habits and chronic medication of the patient.
- Completion of complementary tests (tests, ECG, etc).
- Signature of the anesthetic informed consent.
Through the result of this assessment, a classification of the patient's anesthetic risk is established to assess the risk posed by anesthesia in each specific case.
What is the procedure during surgery?

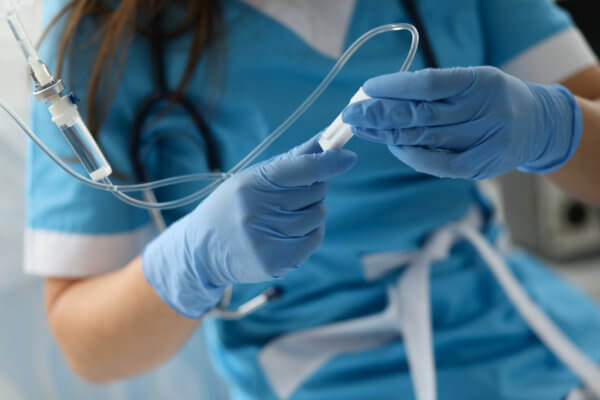
The first step is the intravenous sedation of the patient, so that discomfort is minimized and the patient enters a pleasant state of relaxation and comfort. To achieve this effect, a combination of drugs with different effects is used: anxiolytics, hypnotics and opiates, where the dose and type of anesthetic have been previously established based on the preoperative assessment of the patient.
Afterwards, once the patient is sedated, and a little before starting the surgery, the maxillofacial surgeon performs an infiltration with local anesthetics in the surgical area to intervene. The objective of this infiltration is to achieve complete insensitivity of the area to be treated.

It is also important to know that the anesthesiologist is present throughout the surgery and regulates the level of hypnosis, which can be variable depending on the surgical moment.
Likewise, the patient's breathing and heart rate are monitored throughout the process, in the same way as if they were in the operating room, and oxygen is administered through a cannula of nasal glasses.
How is the postoperative after sedation?
The medication used during surgical sedation is metabolized very quickly, which allows the patient to regain an adequate level of consciousness quite quickly, thus being able to go home without difficulty. If necessary, there are also antagonist drugs that can be administered to more quickly reverse their effect. In addition, the intravenous application of sedatives allows less inflammation during the immediate postoperative period.

The ultimate goal of outpatient surgery is that the patient can go home after the intervention, in a state of lucidity and self-sufficiency, although it is always recommended that they be accompanied by a family member, friend or partner during the postoperative transfer. Likewise, before discharge, it is checked that the patient tolerates oral fluid intake.
In the outpatient surgeries that we perform at the Maxillofacial Institute, we collaborate with the anesthetic team of SEDATIUM, a group of specialists in anesthesiology with a professional experience of more than 15 years in the sector. In this way, we guarantee the safety of our patients and maintain our standards of excellence in all aspects of the procedure.
Related content: